
Stay ahead of the curve with the latest updates from the electric tricycle industry. Follow us to stay informed! Click the ‘Follow’ button below the title to easily access the latest news from the tricycle industry and revisit past highlights from the ‘Historical Messages’ section.
Electric tricycle industry updates are continuously updated. Want to stay ahead of the curve? Follow us to never miss any important news! Additionally, this article will delve into the ‘four key components’ of electric tricycles—the controller, charger, battery, and motor—to help you understand the secrets behind these core components.
1.Electric Tricycle Controller
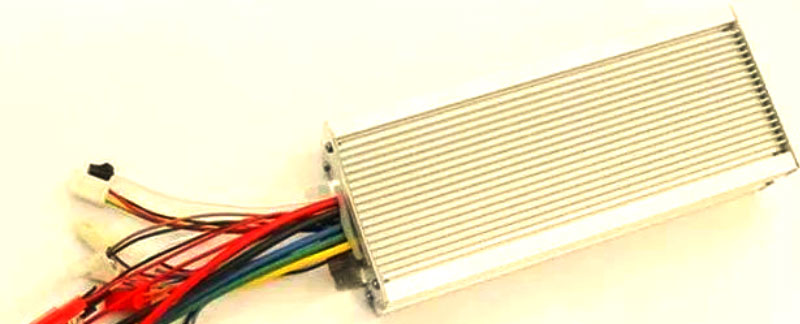
The controller serves as the ‘brain’ of the electric tricycle, responsible for receiving and processing the driver’s commands and controlling the motor’s operation. Its performance directly impacts the vehicle’s driving experience and safety. Therefore, the importance of the controller cannot be overstated when selecting an electric tricycle.
The controller is the core component of the electric tricycle, regulating the output current and voltage of the battery to precisely control the motor’s speed and power, thereby determining the vehicle’s overall speed. The controller features multiple key functions, such as stepless speed regulation, brake power cutoff, current limiting protection, under-voltage protection, speed limiting, speed display, and 1:1 power assistance. There are numerous types of controllers, which can be broadly categorised into brushed controllers and brushless controllers based on their functions and structures. Additionally, the controller’s operating voltage and output power are important parameters. Common voltage specifications include 24V, 36V, 48V, 60V, and 64V, while common output powers include 180W, 250W, 350W, 500W, and 800W, with 350W and 500W controllers being the most widely used.
2.Charger
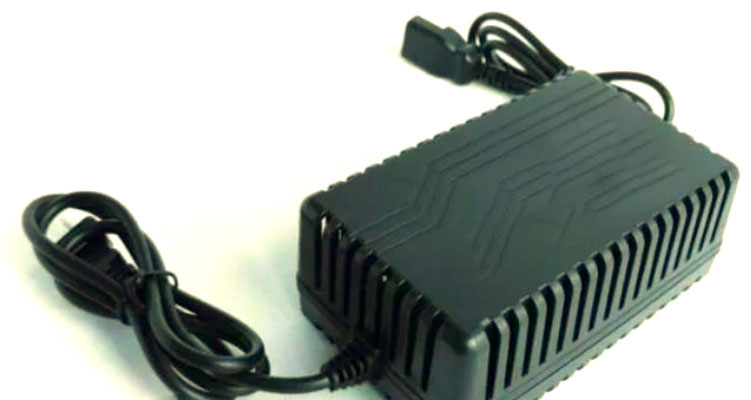

The charger is another critical component in electric tricycles, serving to supply electrical energy to the battery to replenish its power reserves. The charger must be matched to the battery’s voltage and capacity to ensure safe and efficient charging. Additionally, the performance and quality of the charger directly impact the battery’s lifespan and the overall vehicle performance. Common charger types include standard chargers, smart chargers, and fast chargers, each differing in charging speed, safety, and convenience.
As an indispensable component of electric tricycles, the charger’s core function is to replenish the battery’s electrical energy. It efficiently converts mains electricity into direct current and, through precise control of current and voltage, safely and stably stores electrical energy in the battery. The internal structure of a charger is complex, primarily comprising several key components such as rectifier filtering, high-voltage switching, voltage conversion, and electrical control. Its operational process can be divided into three important stages: constant current, constant voltage, and float charging. During the constant current stage, settings are adjusted based on the battery type to ensure compatibility during the charging process. The constant voltage stage is controlled according to battery standards, typically set within a range of 14.7V to 14.8V per cell. The float charge stage also follows battery standards, generally maintaining a voltage of 13.8V to 14V per cell to ensure optimal charging performance.
3.Batteries
Batteries serve as the power source for electric tricycles, and their performance directly impacts the vehicle’s range and service life. Different types of batteries have distinct characteristics, such as lead-acid batteries being cost-effective and easy to maintain, while lithium batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan. When selecting batteries, it is essential to consider both actual requirements and budget. Additionally, proper usage and maintenance practices are critical to ensuring optimal battery performance.
As the power source and energy carrier of electric tricycles, batteries play a central role in driving the motor and providing the necessary operating voltage for the entire vehicle. Battery voltage directly determines the vehicle’s performance, while battery capacity is closely related to its range.
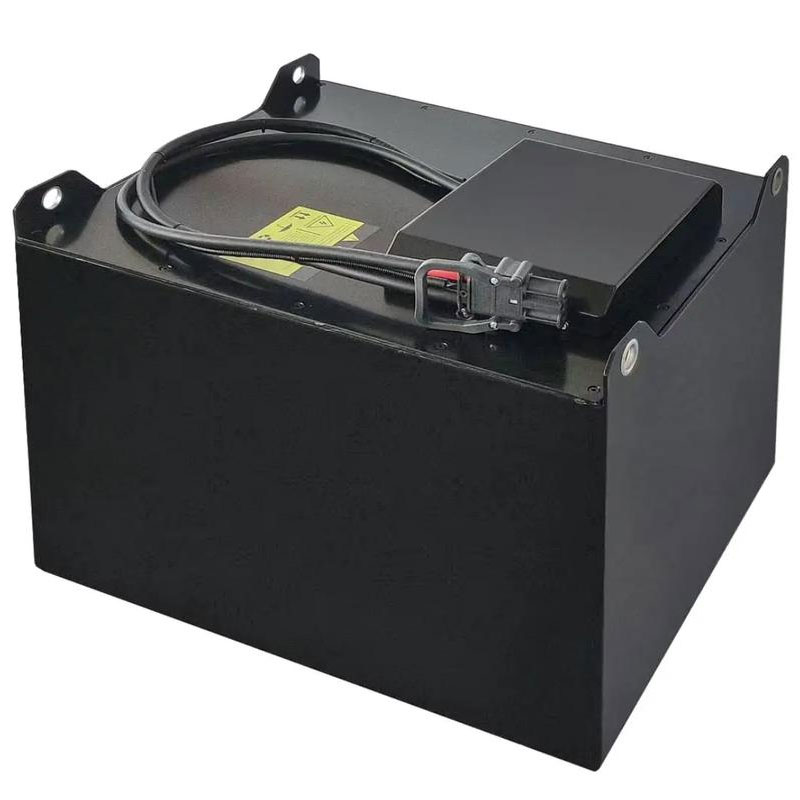

Lead-acid batteries, commonly used in electric tricycles, consist of key components such as the battery casing, positive and negative plates, separators, electrolyte, and terminals. Additionally, there are various types of batteries, including lithium-ion batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, gel batteries, and maintenance-free lead-acid batteries. Among these, gel batteries and lead-acid batteries are the most widely used in electric tricycles.
Furthermore, the voltage and capacity specifications of the battery are also important factors to consider when selecting a battery. In terms of voltage, common options include 12V, 24V, 36V, 48V, and 60V, with electric vehicles typically using 48V and 60V voltage configurations. For capacity specifications, options include 10AH, 12AH, 17AH, 20AH, and 22AH, with electric vehicles commonly using battery capacities of 12AH and 20AH.
4.Motor
The motor is one of the core components of an electric tricycle, responsible for efficiently converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to drive the vehicle. Its performance directly impacts the vehicle’s power output and driving efficiency. In electric tricycles, motors typically use DC motors or AC motors, with DC motors being widely adopted due to their simple structure and ease of maintenance. Additionally, with technological advancements, new high-efficiency motors such as permanent magnet synchronous motors are increasingly being applied in the electric tricycle sector.
The motor is a core component of electric tricycles, responsible for efficiently converting the chemical energy from the battery into mechanical energy. By converting rotational energy into mechanical traction force, the motor drives the wheels to rotate, enabling the vehicle to move. It is worth noting that there is an inverse relationship between the motor’s operating voltage and current, while the motor’s power directly affects its hill-climbing capability.
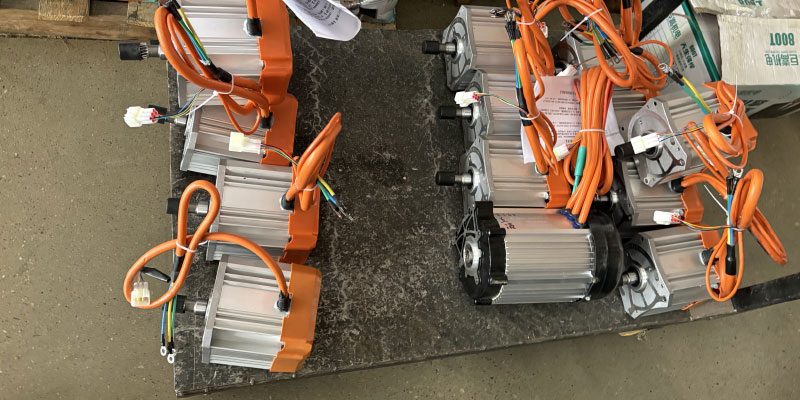

Motors can be broadly categorised into two types: brushed motors and brushless motors. Brushed motors consist of components such as the stator winding, permanent magnet plates, carbon brushes, and commutators, with their operation relying on the alternating contact between the carbon brushes and commutator. Brushless motors, on the other hand, are composed of components such as the stator winding, permanent magnet plates, and Hall effect sensors, with their operation regulated by the Hall effect sensors.
Additionally, motors can be further categorised based on their structure into brushless gearless, brushed gearless, brushless geared, and brushed geared types, among others. Among these, brushless gearless motors are the most widely used in the market. Furthermore, motors offer various voltage options, such as 12V, 24V, 36V, 48V, 60V, and 64V, with the 48V motor being the most commonly used type.
In terms of power, motors can be categorised into multiple grades, such as 180W, 250W, 350W, 500W, 800W, and 1000W, with 350W and 500W motors being the most commonly used in electric tricycles. As electric vehicle technology continues to advance, the performance and quality of these motors have also significantly improved, providing consumers with a safer and more reliable driving experience.
zaoyeo
Over 10 years of experience in the production and design of electric tricycles
